views
The escalating challenges of climate change and environmental degradation have led countries around the world to pursue sustainable solutions to curb greenhouse gas emissions. One such solution is the Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO), a regulatory mechanism aimed at boosting the adoption of renewable energy and reducing carbon emissions.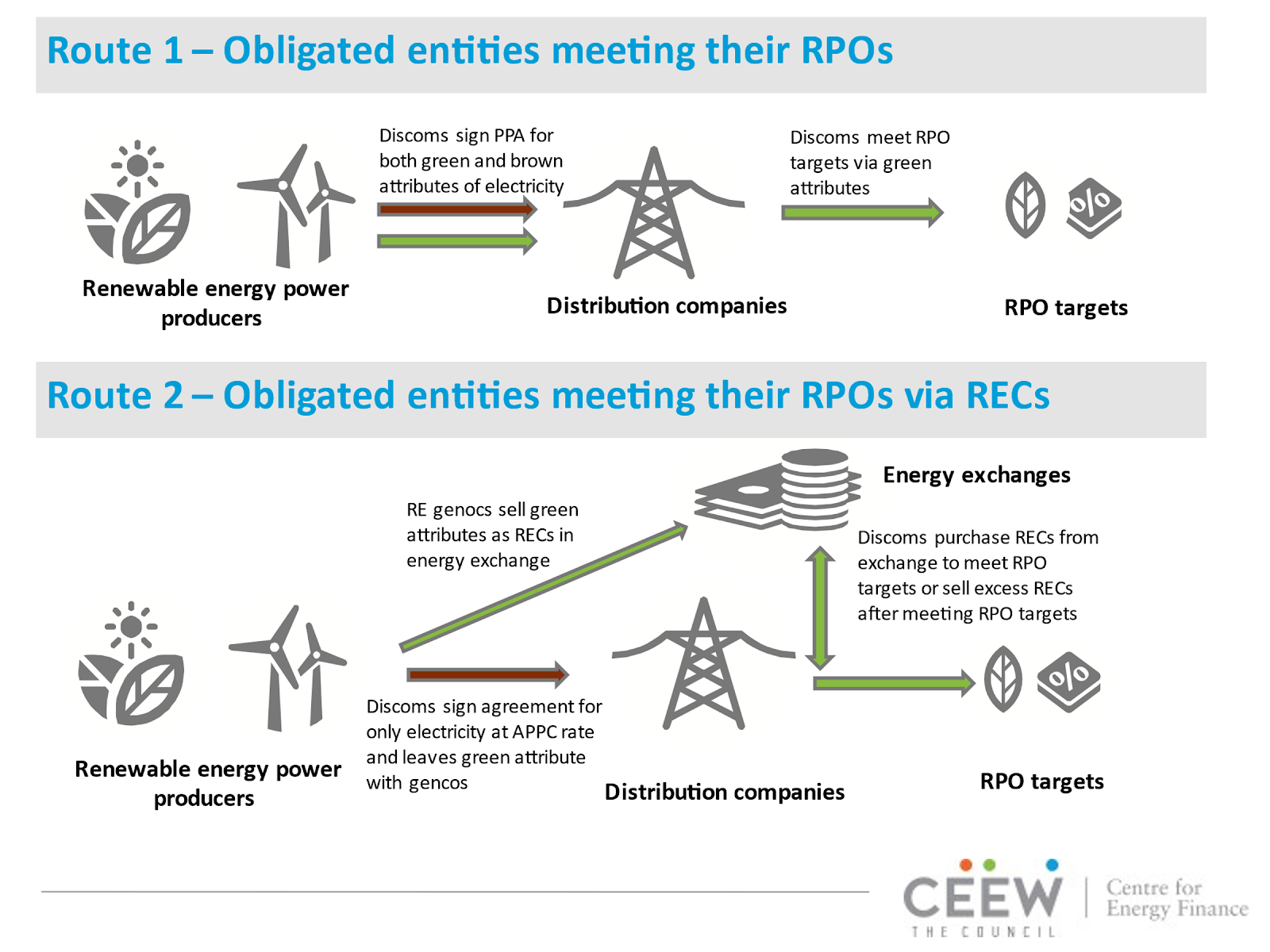
What is Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO)?
Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) is a policy mechanism that mandates electricity distribution companies (DISCOMs), large power consumers, and other obligated entities to source a specified portion of their electricity from renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower. RPOs serve as a regulatory mandate, often enforced by state or national governments, to ensure that a percentage of the power generation mix comes from clean and renewable sources.
The underlying goal of RPOs is to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. By creating a structured obligation for renewable energy procurement, RPOs provide an impetus for the renewable energy market, drive technological advancements, and promote investment in clean energy infrastructure. As a result, RPOs not only help reduce carbon emissions but also support energy security and economic growth.
How RPOs Contribute to Carbon Emissions Reduction?
Carbon emissions from fossil fuels remain one of the leading causes of global warming. Power generation from coal, oil, and natural gas releases significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO₂) into the atmosphere. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is therefore crucial to mitigating climate change. RPOs play a pivotal role in this transition by incentivizing a shift toward cleaner energy options. Here’s how RPOs directly contribute to carbon emissions reduction:
-
Lowering Fossil Fuel Dependence: By mandating a certain percentage of renewable energy in the power generation mix, RPOs reduce the share of electricity generated from fossil fuels. As renewable energy increases in the mix, the reliance on coal and oil decreases, thus cutting down CO₂ emissions.
-
Driving Renewable Energy Projects: RPO requirements lead to increased investment in renewable energy projects, including solar and wind farms. With a stable demand created by RPO compliance, the renewable energy sector can secure financing, develop more projects, and scale up operations, ultimately resulting in higher levels of clean energy generation.
-
Enhancing Carbon Savings Through Green Energy Certificates: Many countries implement RPOs alongside mechanisms like Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) or Green Energy Certificates. These certificates represent units of renewable energy and provide flexibility in meeting RPO targets. By trading these certificates, entities unable to meet their RPO obligations directly can still comply by purchasing certificates, ensuring that emissions reductions are achieved in the broader grid.
-
Encouraging Technological Innovations: RPO policies spur research and development in renewable energy technologies. As the demand for renewables grows, companies invest in improving efficiency and storage solutions, making renewable energy more reliable and cost-effective. This innovation aids the overall reduction of carbon emissions, as renewable energy becomes a more viable alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Benefits of RPOs in Climate Action
The role of RPOs in reducing carbon emissions extends beyond direct climate benefits. RPOs create several indirect benefits that complement the climate action goals:
-
Energy Security: By reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels, RPOs enhance national energy security. Renewable energy sources, which are abundant and domestically available, lessen the risks associated with fluctuating fossil fuel prices and potential supply chain disruptions.
-
Economic Growth and Job Creation: The renewable energy sector is labor-intensive and creates numerous jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. RPOs stimulate local economies, especially in rural areas where renewable projects, like wind farms and solar installations, are often located.
-
Health and Environmental Benefits: Burning fossil fuels releases not only CO₂ but also other pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and particulate matter, which can harm human health. By promoting renewables, RPOs contribute to cleaner air and healthier ecosystems, benefiting public health and biodiversity.
Challenges in Implementing RPOs
While RPOs are effective in driving renewable energy adoption, their implementation comes with challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize their potential in reducing carbon emissions:
-
Compliance Issues: Some obligated entities fail to meet RPO targets, often due to financial or infrastructural constraints. This non-compliance weakens the impact of RPOs on carbon emissions reduction and may require stricter regulatory oversight.
-
Grid Integration of Renewables: Renewable energy sources, especially solar and wind, are intermittent in nature. Integrating them into the grid requires advanced infrastructure and storage solutions, which can be costly and time-consuming to develop.
-
Lack of Awareness and Enforcement: In regions where awareness about RPOs is limited, entities may not prioritize compliance. This calls for increased education, training, and communication about the importance of RPOs for environmental and economic benefits.
-
Market Volatility: Fluctuations in the cost of renewable energy technologies and the market value of Renewable Energy Certificates can impact the feasibility and appeal of meeting RPO targets, particularly for smaller obligated entities.
Future of RPOs in Achieving Carbon Neutrality
As the world moves toward carbon neutrality, RPOs are likely to play an increasingly critical role in decarbonizing the energy sector. Several trends indicate how RPOs will evolve in the future:
-
Higher RPO Targets: Governments may continue to raise RPO targets to accelerate the transition to renewable energy. This shift is essential for meeting the ambitious carbon reduction goals set by international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement and the European Green Deal.
-
Expanded Scope of RPOs: The scope of RPOs may broaden to include new technologies like hydrogen and energy storage, further diversifying the clean energy mix and making it more resilient.
-
Integration with Carbon Markets: As carbon trading gains popularity, RPOs could be integrated with carbon markets, providing obligated entities with additional options to offset emissions and comply with RPO requirements in a flexible manner.
-
Enhanced Accountability Mechanisms: To address compliance issues, governments may implement stricter penalties, incentivize higher compliance rates, and provide financial assistance to entities struggling to meet their obligations.
Conclusion
The connection between Renewable Purchase Obligation (RPO) and carbon emissions reduction is both direct and impactful. By mandating a minimum share of renewable energy, RPOs reduce reliance on fossil fuels, drive investment in clean energy projects, and support technological advancements, all of which contribute to lowering carbon emissions. Despite challenges, RPOs are a powerful tool in the global fight against climate change. With continuous enhancements and stricter targets, RPOs hold the potential to accelerate the shift to renewable energy and enable a low-carbon, sustainable future.





















Comments
0 comment