views
Report Overview:
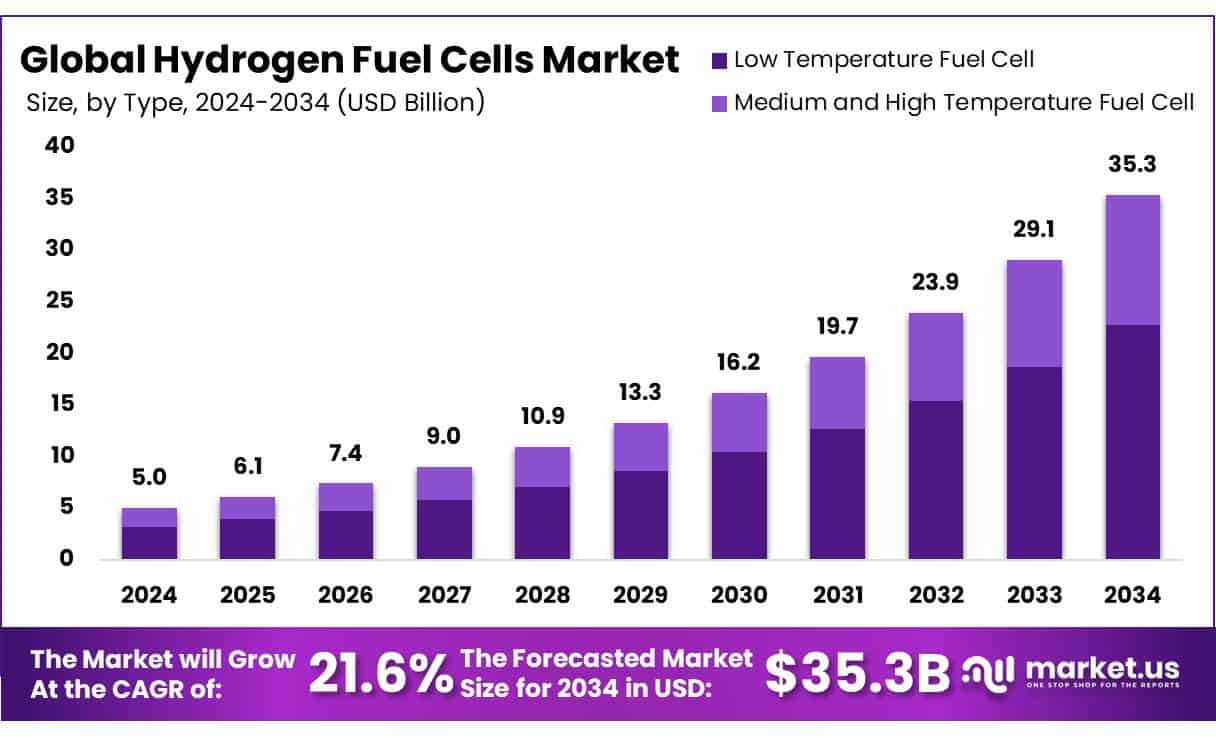
The hydrogen fuel cell market is on a sharp upward trajectory. In 2024, global industry revenues stood at approximately USD 5 billion. Analysts expect compound annual growth of around 21.6% between 2025 and 2034, reaching nearly USD 35.3 billion by 2034.
Growth is being driven by increasing demand for cleaner power solutions across sectors from transportation to stationary power with significant momentum behind low‑temperature technologies and polymer exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs).
These segments are gaining traction in both portable and stationary power applications, particularly where short refueling times and flexible deployment are critical. As governments and corporations shift toward low‑carbon energy systems, hydrogen fuel cells are emerging as a key enabler offering zero-emission operation and versatility that battery‑only systems can’t match.
Key Takeaways:
- The global hydrogen fuel cells market was valued at USD 5.0 billion in 2024.
- The global hydrogen fuel cells market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.6% and is estimated to reach USD 35.3 billion by 2034.
- Among types, low-temperature fuel cells accounted for the largest market share of 67.4%.
- Among technology, Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC) accounted for the majority of the market share at 33.1%.
- By capacity, Above 200 KW accounted for the largest market share of 33.1%.
- By application, stationary accounted for the majority of the market share at 53.1%.
- Among end-use, automotive accounted for the largest market share of 34.1%
- North America is estimated as the largest market for Hydrogen Fuel Cells with a share of 48.2% of the market share.
Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/hydrogen-fuel-cells-market/free-sample/
Key Market Segments:
By Type
- Low-Temperature Fuel Cell
- Medium and High Temperature Fuel Cell
By Technology
- Polymer Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell (PEMFC)
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell (PAFC)
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC)
- Direct Methanol Fuel Cells (DMFC)
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells (MCFC)
- Alkaline Fuel Cell (AFC)
By Capacity
- Up to 50 KW
- 50 to 100 KW
- 100 to 150 KW
- 150 to 200 KW
- Above 200 KW
By Application
- Portable
- Stationary
- Primary
- Back-up
- Combined Heat & Power (CHP)
- Fuel Cell Vehicles
- Light Duty Vehicles
- Medium Duty Vehicles
- Heavy-Duty Vehicles
By End-Use
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
- Marine
- Automotive
- Military & Defense
- Warehouse Logistics
- Others
Drivers:
One of the most significant drivers for the hydrogen fuel cell market is the global shift toward clean and sustainable energy systems. With increasing concerns about carbon emissions and environmental degradation, governments worldwide are pushing for decarbonization across all sectors. Hydrogen fuel cells, which produce electricity through an electrochemical process without harmful emissions, have gained attention as a clean alternative to fossil fuels. In particular, their applications in transportation, stationary power generation, and portable systems make them highly adaptable.
Policy support plays a crucial role in this growth. Incentives, subsidies, and stricter environmental regulations are encouraging industries to invest in hydrogen-based solutions. Additionally, advancements in hydrogen production methods, such as green hydrogen using renewable energy sources, are improving the fuel cell value chain.
The growing demand for energy storage solutions and backup power systems especially in areas with unreliable grids is further pushing adoption. Another factor is the fuel cell’s operational efficiency and quick refueling time compared to batteries, especially in commercial fleets and public transportation. Together, these forces are driving demand, attracting investment, and positioning hydrogen fuel cells as a key technology in the clean energy transition.
Opportunities:
The hydrogen fuel cell market holds strong growth potential through expansion into new geographic regions and industry sectors. Emerging economies are beginning to adopt cleaner energy solutions, and hydrogen fuel cells are well-suited for applications in areas where electricity infrastructure is weak or inconsistent. This includes off-grid communities, mining operations, remote industries, and disaster-prone zones. As awareness grows and technology costs begin to decrease, these markets could become high-growth areas for fuel cell manufacturers and integrators.
Another major opportunity lies in heavy-duty transportation, such as long-haul trucks, marine vessels, and trains, where hydrogen’s high energy density and quick refueling offer advantages over electric batteries. There is also rising interest from commercial and industrial sectors looking for low-emission energy sources that offer resilience and reliability. Telecom towers, hospitals, and data centers are exploring fuel cells for backup power due to their ability to deliver consistent output without emissions.
Restraints:
Despite the promising outlook, the hydrogen fuel cell market faces several limitations that could hinder its growth trajectory. One of the biggest barriers is the high cost of production, both in terms of the fuel cells themselves and the hydrogen fuel required to power them. Hydrogen, especially green hydrogen produced using renewable sources, remains more expensive compared to traditional fuels and even some battery technologies. This makes initial deployment costly and limits accessibility, especially for smaller businesses or public institutions in developing regions.
Infrastructure is another major restraint. The lack of a widespread and reliable hydrogen refueling network discourages potential users, particularly in the transportation sector where range anxiety and fuel availability are significant concerns. Furthermore, the transportation and storage of hydrogen require specialized, high-pressure equipment, which adds complexity and cost to implementation.
Trends:
The hydrogen fuel cell market is experiencing a series of transformative trends that are shaping its future direction. One of the most prominent trends is the global shift toward decarbonization. Countries are committing to net-zero carbon goals, and hydrogen fuel cells are being integrated into national strategies for clean energy transitions. This has accelerated R&D, funding, and pilot projects across diverse sectors, including transportation, industry, and grid-scale energy storage.
Another key trend is the rise of green hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind. Green hydrogen enhances the environmental benefits of fuel cells, making them more appealing to sustainability-focused industries and governments. As production costs for green hydrogen continue to decline, this trend is expected to gain even more momentum.
Market Key Players:
- FuelCell Energy, Inc.
- Ballard Power Systems.
- Cummins Inc.
- SFC Energy AG
- Bloom Energy
- Doosan Group
- Ceres Power Holdings plc
- Plug Power Inc.
- Toshiba Corporation
- AFC Energy
- Panasonic Holdings Corporation
- PowerCell Sweden AB
- Intelligent Energy Limited
- Pearl hydrogen
- Hyster-Yale Group, Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Inocel
- Other Key Players
Conclusion:
The hydrogen fuel cell market is entering a period of robust growth, underpinned by clean‑energy ambitions and clear technical advantages. Moving from niche applications to mainstream acceptance. Low‑temperature and PEMFC technologies are already leading the charge, reflecting a strategic focus on reliable, efficient systems that can scale across sectors.
That said, the journey ahead requires overcoming cost, infrastructure, and market‑share challenges. Continued policy support, along with focused investment in production, distribution and R&D, will be essential. If these pieces fall into place, hydrogen fuel cells may carve out a permanent role in the global energy mix especially in hard‑to‑electrify areas where their advantages are most pronounced. With the right momentum, this market stands ready to become a cornerstone of the low‑carbon future.










