views
When it comes to HVAC systems, one component quietly does a lot of heavy lifting: the condenser coil. Often overlooked by building occupants but crucial to system performance, condenser coils play a central role in cooling, energy efficiency, and equipment longevity. Whether you're an HVAC professional, a facility manager, or simply a curious learner, understanding how condenser coils work—and the different types available—can help you make better decisions when it comes to maintenance, repairs, or upgrades.
What Is a Condenser Coil?
In simple terms, a condenser coil is the part of an HVAC system that releases heat. After refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air, it’s pumped to the condenser coil, typically located in the outdoor unit. Here, the refrigerant releases the absorbed heat into the surrounding air, cools down, and changes from a gas back into a liquid, ready to cycle again.
Without the condenser coil, the system wouldn't be able to reject heat—and that means no cooling indoors.
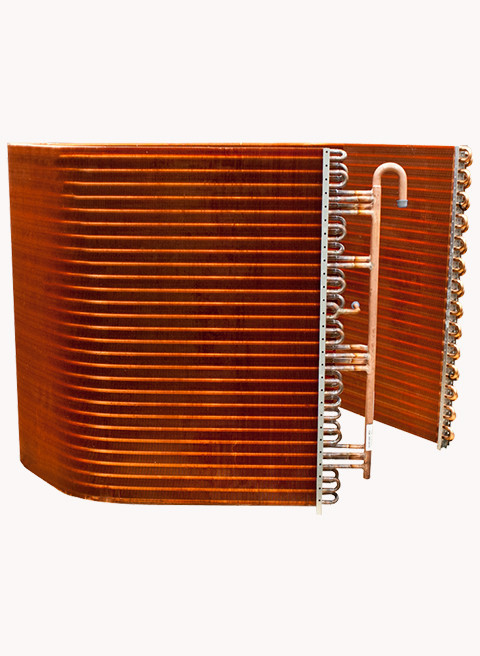
Types of Condenser Coils
Not all condenser coils are made the same. Depending on the application and environment, different types offer distinct advantages.
1. Air-Cooled Condenser Coils
These are the most common in residential and light commercial systems. They use ambient air to remove heat from the refrigerant. Air is typically blown over the coil by a fan.
Pros:
-
Easy to install and maintain
-
No need for water supply
-
Suitable for moderate climates
Cons:
-
Less efficient in hot outdoor temperatures
-
Can be noisy due to fan operation
2. Water-Cooled Condenser Coils
These coils use water instead of air to remove heat. They're often found in larger commercial or industrial buildings.
Pros:
-
More efficient than air-cooled in high-temperature climates
-
Operates quietly
-
Smaller physical footprint
Cons:
-
Requires water supply and a cooling tower
-
Higher maintenance due to water treatment and scaling
3. Evaporative Condenser Coils
A hybrid of air-cooled and water-cooled types, these systems use air and a small amount of water sprayed over the coil to boost cooling.
Pros:
-
Very energy efficient
-
Good for hot and dry climates
Cons:
-
Water usage must be managed
-
Maintenance needed to prevent bacterial growth and scaling
Functions of a Condenser Coil
Condenser coils serve a few key purposes in the cooling cycle:
-
Heat Rejection: They remove heat from the refrigerant and discharge it outdoors.
-
Phase Change: The refrigerant condenses from a high-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid.
-
Cooling Efficiency: The performance of the condenser coil directly affects the system’s efficiency and energy consumption.
In short, if the condenser coil isn't functioning well, neither is your cooling system.
Applications of Condenser Coils
You’ll find condenser coils in a wide range of HVAC and refrigeration systems, including:
-
Residential air conditioners
-
Commercial rooftop units
-
Refrigerated display cases and cold rooms
-
Chillers and industrial HVAC systems
-
Heat pumps
Each application might require a slightly different coil design, material, or configuration based on load, environment, and usage.
Common Materials Used
-
Copper tubes with aluminum fins – The most common and cost-effective design
-
All-aluminum coils – Lightweight and corrosion-resistant
-
Microchannel coils – High efficiency and compact design, often used in modern systems
Maintenance Tips for Long Life
Even the best-designed condenser coil won’t last long without proper care. Here are a few tips:
-
Clean the coil regularly to remove dirt, leaves, and debris.
-
Check for refrigerant leaks or damage to the fins.
-
Inspect the fan motor and ensure good airflow.
-
Use coil cleaners that are safe for the material to avoid corrosion.
Regular maintenance not only extends the life of the coil but also improves efficiency and reduces energy bills.
Conclusion
The condenser coil may be just one part of a complex HVAC system, but its role is vital. By understanding its types, functions, and applications, you're better equipped to troubleshoot issues, plan maintenance, or select the right system for your space. Whether it's air-cooled, water-cooled, or evaporative, the right condenser coil can make a world of difference in system performance and durability.
Stay cool—because behind every comfortable room is a hardworking coil.






















Comments
0 comment