views
link between kidney stones and erectile dysfunction
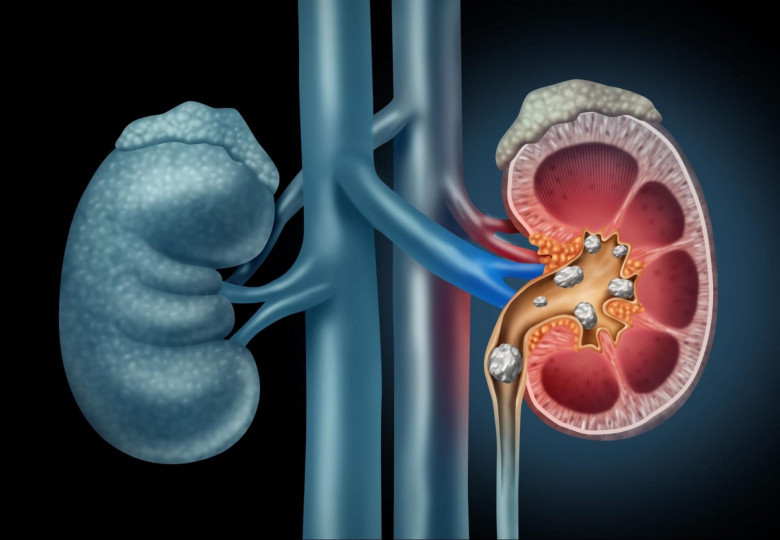
Kidney stones and erectile dysfunction (ED) may seem like unrelated health issues at first glance, but emerging evidence suggests that there could be a connection between the two. Both conditions are relatively common and can cause significant discomfort and distress, but what many people don’t realize is that the presence of kidney stones could potentially have an impact on sexual health.
In this blog, we’ll explore the link between kidney stones and erectile dysfunction, looking at how these conditions might be connected, the possible underlying causes, and what individuals can do to improve their overall health and well-being.
Understanding Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. They can vary in size, from tiny grains to large, painful stones that require medical intervention. Kidney stones are typically composed of calcium, oxalate, uric acid, or phosphate. The most common symptoms of kidney stones include:
- Severe pain in the lower back or abdomen (often referred to as renal colic)
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination or urgency
- Nausea and vomiting
While most kidney stones can pass naturally through the urinary tract, larger stones may require medical treatments such as shock wave therapy, surgery, or medication.
Is Viagra harmful to kidneys?
Viagra is a medication like Vidalista 60 used to treat erectile dysfunction, but many people wonder if it's harmful to the kidneys. While studies have shown that Viagra can increase blood flow to the kidneys, there is no evidence that it causes kidney damage.
However, individuals with kidney disease or those taking Cenforce 150 medications that affect the kidneys should talk to their doctor before taking Viagra, as it may not be safe for them. As with any medication, it's important to use Viagra as directed and discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. When used appropriately, Viagra can be an effective treatment option for those with erectile dysfunction.
What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. ED can be caused by various factors, including psychological, physical, and lifestyle-related issues. Physical causes are often related to poor blood flow, hormone imbalances, or nerve damage.
Common physical causes of ED include:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Hormonal imbalances
How Kidney Stones and Erectile Dysfunction Might Be Connected
While kidney stones and erectile dysfunction are separate medical conditions, certain factors can make them interrelated. Here’s how kidney stones might contribute to ED:
1. Pain and Stress: The Impact of Kidney Stone Pain on Sexual Function
The pain associated with passing or having kidney stones can be excruciating, often leading to significant discomfort that can last for hours or even days. Chronic pain, whether from kidney stones or other health conditions, can interfere with sexual function by increasing stress and anxiety levels.
When a person is in pain, their body releases stress hormones such as cortisol, which can interfere with normal hormonal balance. Stress and anxiety can also lead to mental distractions, lowering libido and making it difficult to focus on sexual activity. Chronic pain can lead to depression or a lack of interest in sex, contributing to the development of erectile dysfunction.
2. Increased Risk of Underlying Health Conditions
Kidney stones are often linked to other health conditions, many of which are also associated with erectile dysfunction. For example, obesity, high blood pressure, and diabetes are risk factors for both kidney stones and erectile dysfunction.
- Obesity increases the likelihood of both developing kidney stones and experiencing ED. Obesity is a risk factor for both cardiovascular disease and diabetes, which can impair circulation and lead to erectile dysfunction.
- High blood pressure can damage blood vessels, including those that supply the penis, reducing blood flow and contributing to ED. High blood pressure is also a risk factor for kidney stones, particularly those caused by calcium deposits.
- Diabetes is a leading cause of erectile dysfunction, as it can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow to the penis. Diabetic individuals are also more prone to developing kidney stones, particularly uric acid stones.
3. Medications Used to Treat Kidney Stones
Some medications used to treat kidney stones can have side effects that affect sexual health. For instance, certain painkillers or medications for high blood pressure may have erectile dysfunction as a known side effect.
- Pain relievers: Opioids and other strong pain medications are often prescribed to manage the pain from kidney stones. These drugs can affect blood flow and lower testosterone levels, contributing to erectile dysfunction if used over time.
- Diuretics and calcium channel blockers: These medications, which are used to treat high blood pressure and prevent kidney stones, can interfere with the function of blood vessels, causing erectile issues.
It’s important for individuals taking medications for kidney stones to talk to their doctor about any potential side effects related to sexual health and explore alternative treatments if necessary.
4. Nerve Damage
In some cases, kidney stones can lead to nerve damage. This is especially true for individuals who have recurrent kidney stones or have had kidney stones that required surgical intervention. Nerve damage can affect both urinary and sexual function, leading to erectile dysfunction. Nerve damage in the pelvic region can interfere with the body’s ability to respond to sexual stimulation and affect blood flow to the penis.
Can Treating Kidney Stones Improve Erectile Dysfunction?
In some cases, addressing kidney stones may help alleviate erectile dysfunction, especially if the ED is primarily related to pain or stress caused by the stones. When kidney stones are treated and pain is managed effectively, individuals may experience less stress and improved sexual function. However, if the ED is caused by underlying conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or obesity, treating the kidney stones alone may not be enough to resolve the erectile dysfunction.
In addition to treating kidney stones, individuals experiencing ED should consider lifestyle changes that can improve both kidney and sexual health, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly can help prevent both kidney stones and ED.
- Managing blood pressure and diabetes: If you have high blood pressure or diabetes, working with a healthcare provider to control these conditions can improve both kidney function and erectile health.
- Reducing stress: Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being, potentially improving erectile function.
Conclusion
While kidney stones and erectile dysfunction are separate medical conditions, they can be interlinked through common risk factors, underlying health conditions, and the impact of pain and stress. It’s important for individuals who experience both kidney stones and ED to seek medical advice to address both conditions comprehensively. Managing underlying health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure, along with lifestyle changes and proper treatment, can help improve overall health and alleviate symptoms of both kidney stones and erectile dysfunction.
If you’re struggling with either condition, consulting a healthcare provider can provide the necessary guidance and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.






















Comments
0 comment