views
Introduction
Airway management is an important component of surgery and emergency treatment, and the Endotracheal Tube Uncuffed is an essential device for patient protection while on ventilation. With no inflatable cuff, this tube is especially used in pediatric and neonatal treatment. Quality and accuracy are at the center of every medical device at GST Corporation Ltd, including the Endotracheal Tube Plain model.
This article describes the required characteristics, uses, benefits, and implications of uncuffed ET tube usage to assist healthcare providers with informed decision-making for airway devices.
What Is an Endotracheal Tube Uncuffed?
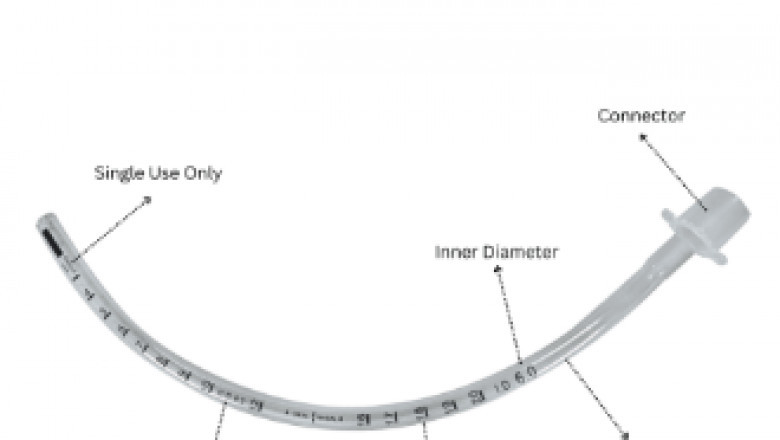
An uncuffed tracheal tube is an endotracheal tube that does not have a cuff or inflatable balloon at the distal end. In contrast to cuffed tubes, which close off the airway and do not allow air leakage, uncuffed tubes depend on a close fit inside the trachea, particularly beneficial for neonates and pediatric patients where airway tissues are more fragile.
Key Features of an Uncuffed Endotracheal Tube
Here are the standout features of a high-quality ET Tube Uncuffed:
-
Non-toxic, medical-grade PVC: Ensures biocompatibility and patient safety.
-
Smooth beveled tip: Minimizes trauma during insertion.
-
Clear, transparent body: Allows visual inspection of blockages and condensation.
-
Markings for depth: Helps position the tube correctly in the trachea.
-
Radio-opaque line: Enhances visibility under X-ray for accurate placement
-
Color-coded connectors: Aids in size identification quickly.
Common Uses and Applications
The endotracheal tube uncuffed is most commonly used in:
-
Neonatal and pediatric ventilation
Children under 8 years of age typically have smaller airways that may be injured by cuffed tubes. The uncuffed variety minimizes trauma while maintaining effective ventilation. -
Short surgical procedures
When patients need airway access for a limited time, the use of a plain endotracheal tube reduces complications related to cuff pressure. -
Patients with sensitive airways
In cases where inflammation or trauma to the airway must be avoided, uncuffed tubes are a safer option.
Advantages of Using ET Tube Uncuffed
Choosing the right airway equipment is essential for optimizing patient outcomes. Here are the benefits of endotracheal tubes plain or uncuffed:
-
Less risk of airway injury: Without a cuff, the risk of tracheal mucosal damage or ischemia is significantly reduced.
-
Simplified insertion process: Especially useful in emergencies or neonatal resuscitation.
-
Cost-effective: Lower manufacturing complexity can reduce overall hospital costs.
-
Improved comfort: Patients often experience fewer postoperative sore throat symptoms with uncuffed tubes.
How to Choose the Right Uncuffed Tracheal Tube
Several factors influence the choice of an uncuffed tracheal tube, including:
-
Patient Age & Size: Pediatric and neonatal patients typically require smaller diameter tubes.
-
Procedure Duration: Shorter procedures favor uncuffed tubes; longer procedures may require careful consideration.
-
Airway Anatomy: Any abnormalities or obstructions should be evaluated before selection.
-
Ventilation Needs: Adequate ventilation should be confirmed post-insertion using capnography or chest movement.
Insertion Technique: Best Practices
-
Pre-check the equipment: Ensure the ET tube is sterile and intact.
-
Position the patient: Align the head and neck to allow better access to the airway.
-
Use of laryngoscope: A direct visual guide aids in smooth insertion.
-
Confirm placement: Through auscultation, chest rise observation, and capnography.
-
Secure the tube: Use tape or a tube holder to prevent dislodgement.
Comparison: Cuffed vs. Uncuffed Endotracheal Tubes
Safety and Sterilization Standards
The endotracheal tube uncuffed must comply with international safety standards such as ISO and CE certification. GST Corporation Ltd ensures that all products, including plain endotracheal tubes, are:
-
Sterilized using ethylene oxide (EO)
-
Individually packed in peel-open pouches
-
Free from latex, phthalates, and other harmful materials
Global Demand and Importance
With increasing demand for safe pediatric airway management, the uncuffed tracheal tube is gaining widespread global usage. Medical professionals and hospitals across the world trust standardized products that guarantee:
-
High performance
-
Smooth intubation
-
Safe ventilation outcomes
Conclusion
An Endotracheal Tube Uncuffed is a vital tool in pediatric and emergency airway management. Designed for precision and patient comfort, it offers multiple benefits in neonatal and short-term ventilatory support. Whether you're dealing with routine procedures or critical interventions, choosing a reliable and standardized ET tube uncuffed can make a significant difference.
Explore more about the product and its specifications at GST Corporation Ltd, where medical innovation meets international standards.





















Comments
0 comment