views
Cancer remains one of the most formidable health challenges of our time. While advancements in treatment have improved survival rates, early detection remains the cornerstone of saving lives. When cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, patients often have more treatment options, less invasive procedures, and significantly better outcomes. Traditional methods of detecting cancer through medical imaging—such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and mammograms—have saved countless lives, but they are not perfect. Human radiologists, despite their expertise, face challenges like fatigue, high workloads, and the difficulty of spotting subtle anomalies in complex images. This is where artificial intelligence (AI) is stepping in, transforming the landscape of early cancer detection and offering hope for a future where more cancers are caught in time.
The Critical Role of Early Detection
Early detection can dramatically alter a patient’s prognosis. For example, the five-year survival rate for breast cancer detected at stage 1 is over 99%, compared to 30% for stage 4. Similarly, lung cancer survival rates jump from 6% at advanced stages to 60% when caught early. However, identifying tiny tumors or precancerous lesions is incredibly challenging. Radiologists must examine hundreds of scans daily, often under time constraints, increasing the risk of oversight. AI addresses these limitations by enhancing accuracy, speed, and consistency in analyzing medical images.
AI’s Breakthroughs in Medical Imaging
AI systems, powered by machine learning and deep learning algorithms, excel at recognizing patterns in vast datasets. When trained on millions of medical images, these tools learn to detect abnormalities that might escape even the most experienced human eyes. Here’s how AI is making a difference:
1. Enhanced Precision in Identifying Abnormalities
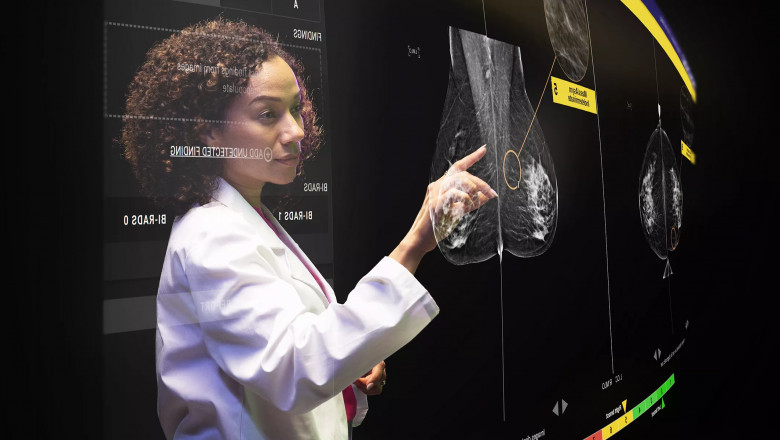
AI algorithms analyze medical images at a pixel level, scrutinizing textures, shapes, and densities that humans might overlook. For instance, in mammography, AI can distinguish between benign calcifications and malignant tumors with remarkable accuracy. Recent studies show that AI models can identify early signs of lung cancer in CT scans years before symptoms manifest, enabling interventions at stages when tumors are still treatable.
These systems also reduce variability in diagnoses. Unlike humans, whose assessments may differ based on experience or fatigue, AI delivers consistent evaluations, ensuring that a scan analyzed at midnight receives the same scrutiny as one reviewed at noon.
2. Reducing Diagnostic Errors
False negatives—missed cancers—are a critical concern in radiology. A radiologist reviewing dozens of scans in a single shift might inadvertently overlook a small lesion or dismiss it as harmless. AI acts as a safety net, flagging suspicious regions for closer inspection. For example, in prostate cancer screening, AI tools analyze MRI scans to highlight areas likely to harbor tumors, guiding biopsies more effectively. This collaborative approach minimizes missed diagnoses and ensures patients receive timely follow-up care.
3. Accelerating Workflows
In emergencies or high-volume settings, speed is vital. AI can prioritize urgent cases, such as identifying brain hemorrhages in CT scans within seconds, or process routine screenings faster than humanly possible. This efficiency is particularly impactful in regions with shortages of radiologists. In rural or underserved areas, AI-powered tools enable clinics to screen more patients without delays, bridging gaps in healthcare access.
4. Predicting Cancer Risk and Progression
Beyond detection, AI is venturing into predictive analytics. By analyzing historical imaging data and patient records, algorithms can estimate an individual’s likelihood of developing certain cancers. For instance, AI models trained on mammograms and genetic data can predict breast cancer risk years in advance, prompting preventive measures like lifestyle changes or increased monitoring. Similarly, some tools analyze tumor features in imaging to forecast how aggressively a cancer might grow, helping doctors tailor treatment plans.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI’s potential is immense, its integration into healthcare requires careful navigation of several challenges:
- Data Quality and Diversity: AI systems depend on large, diverse datasets to perform accurately. If trained predominantly on images from specific demographics (e.g., a single ethnic group or geographic region), they may underperform for underrepresented populations. Ensuring inclusive datasets is essential to avoid biased outcomes.
- Regulatory and Ethical Standards: Regulatory bodies are working to establish guidelines for AI in healthcare. Issues like patient privacy, transparency in decision-making, and accountability for errors must be addressed to build trust among providers and patients.
- Human-AI Collaboration: AI is not meant to replace radiologists but to augment their skills. Clinicians must remain central to decision-making, interpreting AI-generated insights in the context of a patient’s overall health. Training healthcare workers to use AI tools effectively is critical.
The Future of AI in Oncology
The next wave of innovation lies in combining AI with emerging technologies. For example:
- Integration with Wearable Devices: AI could analyze data from wearable sensors to detect early signs of cancers, such as skin changes indicative of melanoma.
- 3D Imaging and Virtual Biopsies: Advanced AI models are being developed to create 3D reconstructions of tumors from imaging data, allowing “virtual biopsies” that reduce the need for invasive procedures.
- Global Democratization of Screening: Portable, AI-powered ultrasound devices and smartphone-based tools could bring cancer screening to remote areas, saving lives in regions lacking advanced medical infrastructure.
Conclusion: A New Era of Proactive Healthcare
AI’s role in early cancer detection marks a paradigm shift from reactive to proactive medicine. By catching tumors earlier, reducing diagnostic errors, and personalizing risk assessments, this technology is empowering healthcare providers to act before cancer progresses. For patients, this means less invasive treatments, better survival rates, and more years of healthy life.
However, the success of AI hinges on collaboration. Clinicians, researchers, policymakers, and technologists must work together to ensure these tools are ethical, equitable, and aligned with the goal of patient-centered care. As AI continues to evolve, its greatest impact may lie not in replacing human expertise but in amplifying it—giving doctors the tools they need to fight cancer with unprecedented precision and compassion.
In the end, AI is more than a technological marvel; it’s a lifeline for millions, offering hope that cancer’s deadliest stages may one day become a rarity rather than a reality.





















Comments
0 comment