views
Robotic Surgery
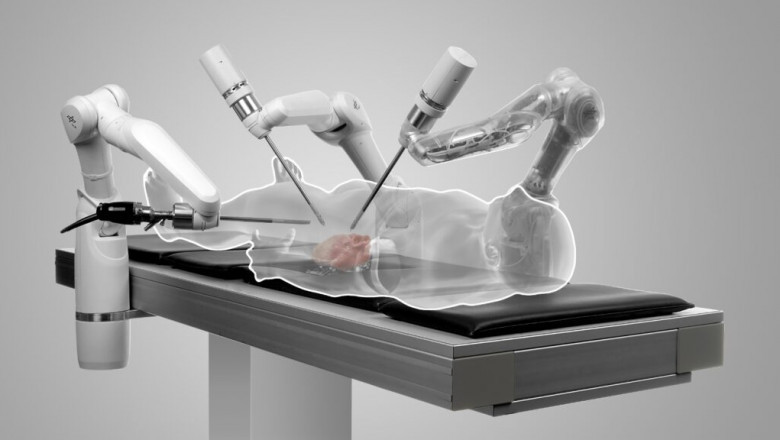
Robotic surgical systems have revolutionized many areas of medicine by enabling minimally invasive procedures through small incisions. Da Vinci, the leading brand of surgical robot, is used for procedures like prostatectomies, hysterectomies, cardiac surgery and more. The Da Vinci features three or four robotic arms controlled by a surgeon sitting at a console several feet away from the patient. The surgeon's hand and wrist movements are translated into precise movements of miniature robotic instruments inside the patient. Some key benefits of robotic surgery include:
Robotic systems allow surgeons to operate through smaller incisions compared to open surgery, resulting in less pain, blood loss, scarring and faster recovery times for patients. The console provides surgeons with a high-definition, 3D view of the surgical site during procedures. Hand tremors are filtered out, allowing for even finer control and precision compared to traditional laparoscopic techniques. Certain complex operations may be easier to perform robotically due to the enhanced dexterity and range of motion provided by the systems.
Medical Robots surgery is most commonly used for urological and gynecological procedures but is expanding into other areas as well. As of 2018, over 5 million robotic surgeries had been performed worldwide. While still fairly expensive for hospitals, robotic systems have contributed significantly to improved patient outcomes for many conditions. Ongoing research aims to further expand the types of procedures that can be performed robotically.
Surgical Assistants
Some robot models are being developed to serve as intelligent assistants during surgery rather than replacing the human surgeon entirely. The Raven surgical robot from Baltimore-based TransEnterix features articulating arms that hold and manipulate surgical tools under the direction of the operating surgeon. The System seamlessly translates the surgeon’s hand movements performed at a console into precise movements of the robotic tools inside the patient.
Another new robotic system is the da Vinci SP surgical platform which features a dual-console configuration for telesurgery applications. The SP allows an expert surgeon at one location to guide a less experienced surgeon or resident at another site, enabling knowledge sharing and proctoring during live operations. This “trainer-trainee” dynamic could help address disparities in surgical expertise available in different regions of the world. Robotic assistants allow teams of human surgeons to work together more efficiently and help extend surgical expertise into remote or underserved areas.
Rehabilitation Medical Robots
Rehabilitation robotics aims to augment traditional physical, occupational and speech therapies using robotic devices and interactive virtual reality systems. Certain robot models can be used to move patients' limbs through repetitive exercises that help regain mobility after injuries, strokes or other disabling conditions. For example, the Lokomat robotic gait orthosis is used in physiotherapy to help retrain normal walking patterns. The patient wears an exoskeleton-type frame that gently guides their legs through the walking motions while supported in an upright posture on a treadmill. Therapists can adjust the level of assist provided by the robots to gradually challenge patients as their strength returns.
Other robots target recovery of hand and arm functions through grasping and range-of-motion exercises. The ArmeoPower exoskeleton suit, for instance, challenges patients to complete interactive gaming tasks that train gripping, reaching and coordination. Some stroke rehabilitation robots use virtual reality environments to motivate patients through tasks simulated in 3D worlds. Early evidence suggests robotic therapies may help improve outcomes when combined with traditional therapies by facilitating more intense, personalized practice sessions. As the technology advances, rehabilitation robots will likely play an increasingly important supporting role in returning functionality to patients.
Medical Robots Companions
While robots are clearly advancing healthcare through surgery and rehabilitation, they are also being developed as companions for older adults and those living with chronic medical conditions. Companion robots aim to provide benefits like reduced loneliness, increased social interaction, and assistance with activities of daily living. For example, Paro is a therapeutic robotic seal designed to provide comfort through cuddling and responding to touch and voice. Preliminary research found Paro helpful for reducing stress and agitation in elderly dementia patients.
Anthropic's helps older adults stay active and engaged by suggesting light physical activities and facilitating video calls with family and friends. Other social robots under development converse through intelligent voice interfaces and have expressive faces, aiming to establish more natural human-robot relationships over time. As these technologies mature, companion robots may play a greater role in supporting independent living and improving quality of life, especially for those managing multiple chronic conditions who require frequent check-ins or assistance.
Choose preferred language for better understanding-
About Author-
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. With an MBA in E-commerce, she has an expertise in SEO-optimized content that resonates with industry professionals. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)





















Comments
0 comment