views
Sustainability has become a core focus of the food and beverage industry in a world that's increasingly aware of its environmental footprint. One innovative concept gaining momentum in this space is culinary upcycling. This idea challenges traditional food production processes by turning food waste or by-products into high-value, usable ingredients. Culinary upcycling not only helps reduce food waste but also plays a pivotal role in making the food industry more sustainable, while creating new business opportunities.
In this blog, we'll explore culinary upcycling, its environmental benefits, market potential, key players, challenges, and the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
Understanding Culinary Upcycling?
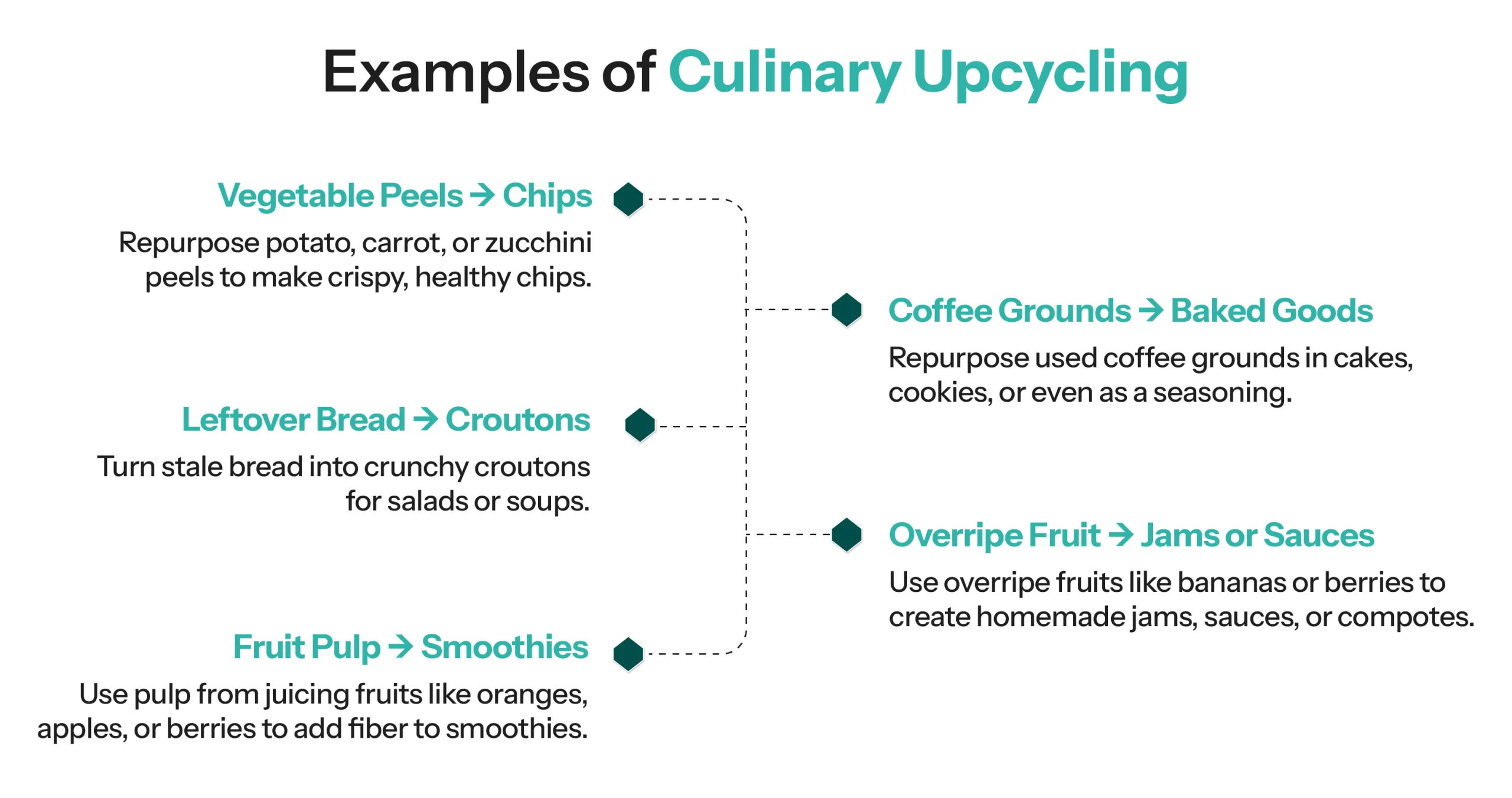
Culinary upcycling involves transforming food by-products or what would traditionally be considered waste into new, nutritious, and delicious products. These by-products are often created during food production, processing, or preparation, including fruit peels, vegetable scraps, stems, seeds, or even spent grains from beer production.
Rather than being discarded, these food scraps are repurposed into innovative products, ranging from snacks, beverages, and even entire meals. Not only does this help reduce waste, but it also creates new food items that are both delicious and resource-efficient.
Take, for example, the use of overripe bananas. Instead of throwing them out, these bananas can be turned into smoothies, energy bars, or banana-based flour. Similarly, by-products from brewing beer, like spent grains, can be used to make upcycled granola or high-protein bread.
The Sustainability Factor: Why It Matters
As the world faces increasing environmental challenges, reducing food waste is one of the most impactful ways to lessen the strain on the planet. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced globally is wasted, contributing to significant carbon emissions and waste in landfills. In fact, food waste is responsible for about 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
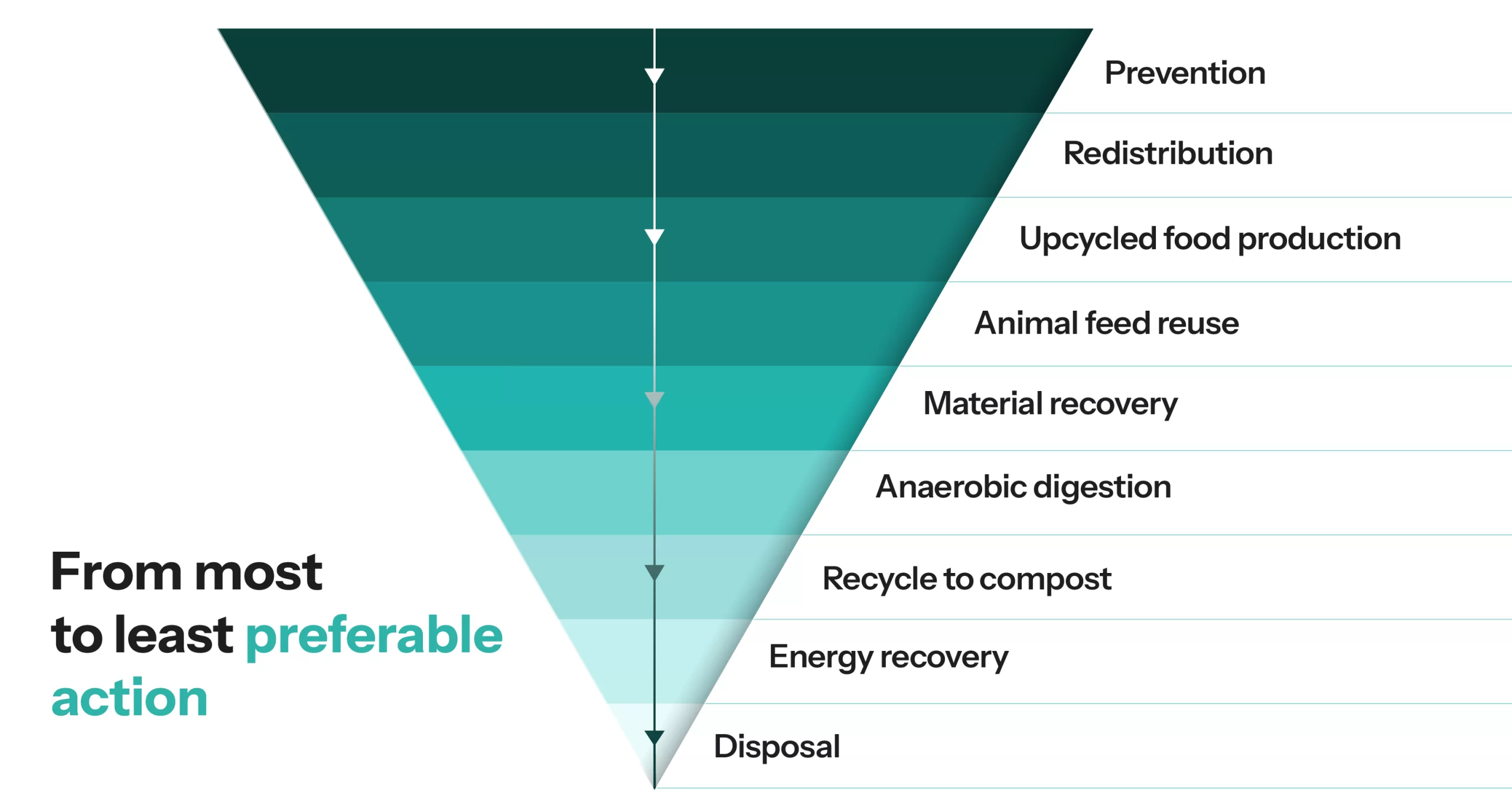
Culinary upcycling directly addresses these issues by utilizing food that would otherwise end up in the trash, cutting down on both food waste and the resources required to produce new food. Additionally, upcycling contributes to a circular economy, where waste is minimized, and resources are continually repurposed to reduce environmental impact.
For example, when food by-products are used in the creation of new food products, it reduces the need for raw materials, water, and energy that would otherwise go into growing new ingredients. The process of upcycling can thus significantly lower the food industry's carbon footprint.
Market Size & Growth Potential
The concept of culinary upcycling isn't just an environmental movement but a rapidly growing market. Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of food waste, and many are seeking more sustainable and ethical food choices. The global sustainable food market is estimated to reach $1.2 trillion by 2030, with upcycled food products gaining a solid foothold in this landscape.
Consumer Trends are aligning perfectly with the upcycling movement. With more people adopting plant-based diets, focusing on clean labels, and preferring eco-friendly products, there has been a surge in demand for upcycled food items. Younger generations, especially Gen Z and Millennials, are particularly invested in sustainability and ethical consumption, driving companies to embrace upcycling as a key part of their brand story.
As the market expands, more companies are recognizing the opportunity to create innovative upcycled products. These include everything from upcycled snack bars, beverages, and chips to upcycled oils, flours, and even pet food. The market for upcycled food is projected to grow significantly in the coming years as consumers and businesses alike embrace its benefits.
Key Players in the Culinary Upcycling Industry
As the movement gains traction, several innovative companies and chefs are leading the way in culinary upcycling.
Upcycled Food Association (UFA), for example, is a prominent organization in the space. It promotes the development and scaling of upcycled food products, offering certifications to businesses that produce them sustainably. Some of the standout brands in the upcycling world include:
- Toast Ale: This brewery has found a way to reduce food waste by using surplus bread to brew their beer. It's a creative example of how food waste can be transformed into something new and enjoyed by consumers.
- ReGrained: ReGrained takes spent grains from the beer-making process and upcycles them into high-protein, fiber-rich snacks such as granola bars. The company is a prime example of how food by-products can be transformed into healthy, marketable products.
- Rebel Kitchen: Rebel Kitchen creates upcycled coconut milk from leftover coconuts that might otherwise be discarded. Their products are environmentally friendly and in demand due to their focus on health and sustainability.
Additionally, restaurants and chefs like Dan Barber, known for his sustainability efforts at Blue Hill at Stone Barns, are making culinary upcycling part of their dining experience. Barber's work shows that chefs can creatively use upcycled ingredients to elevate the dining experience while contributing to food waste reduction.
Benefits of Culinary Upcycling
There are numerous benefits to embracing culinary upcycling, ranging from environmental to economic to nutritional advantages.
1. Environmental Benefits:
- Reduction in Food Waste: Upcycling directly addresses the global issue of food waste by reusing ingredients that would otherwise be discarded.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: By using food by-products, the carbon emissions tied to food production (including water and land usage) are significantly reduced.
2. Economic Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Upcycled ingredients are often cheaper than traditional ones, as they are by-products from other industries (such as brewing or juicing).
- New Revenue Streams: Food businesses can tap into a growing market for sustainable products, generating new income from products like upcycled snacks or drinks.
3. Health and Nutrition:
- Nutrient Density: Many upcycled ingredients, like fruit peels or spent grains, are rich in nutrients and fiber. This can provide consumers with a healthier alternative to processed foods.
- Innovation in Food Creation: Upcycled products encourage food innovation, offering exciting new flavors, textures, and possibilities for both chefs and consumers.
Challenges in Culinary Upcycling
While the concept of culinary upcycling holds great promise, some challenges must be addressed:
1. Consumer Perception:
Some consumers still associate food waste with lower quality or less appetizing food. Education is essential to shift the mindset and promote the value of upcycled ingredients.
2. Supply Chain Issues:
Consistently sourcing high-quality by-products for upcycling can be a logistical challenge. Ensuring that these ingredients meet health and safety standards is vital to gaining consumer trust.
3. Regulation & Certification:
The lack of clear guidelines and certifications for upcycled food can be a barrier. Establishing universal standards and certifications will help to improve the transparency and credibility of upcycled food products.
The Future of Culinary Upcycling
Looking ahead, the possibilities for culinary upcycling are vast. As technology advances, we could see even more innovative ways to upcycle ingredients, including through:
Advanced Food Technologies: Emerging technologies like fermentation or biorefining could help process by-products more efficiently, creating entirely new classes of upcycled foods.
Upcycled Meal Kits and Ready-to-Eat Products: As consumer demand for convenient, sustainable food grows, companies may begin offering upcycled meal kits or ready-to-eat meals, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional fast food.
Global Expansion: The upcycling movement has the potential to expand globally, with regions facing food security challenges, particularly benefiting from creative ways to reuse local by-products and reduce waste.
Conclusion
Culinary upcycling offers a sustainable, innovative solution to the pressing problem of food waste. With the growing demand for eco-friendly products, it is quickly becoming a key trend in the food industry. By repurposing food by-products into new, nutritious, and tasty offerings, the culinary world is embracing a future where waste is minimized and resources are maximized. As more businesses and consumers take part in this movement, culinary upcycling could become a major part of the global solution to sustainability in food production.
Are you ready to join the upcycling revolution? Whether you're a food manufacturer, restaurant owner, or consumer, the future of food is looking more sustainable and delicious than ever before.






















Comments
0 comment