views
Future of Medicine | 3D and 4D Printing Innovations
3D printing technology, also known as additive manufacturing, is a digitally controlled technique of fabricating a product by layer-wise addition of the feed material to generate complex geometric structures. This technique has wide applications in the fields of mechanics, consumer goods, electronics, aeronautics, medicine, the food industry, and various other fronts.
The manufacturing process of pharmaceuticals has progressed from batch process to continuous process and now to printing.3D printing technology started gaining increased attention in the pharmaceutical field after the USFDA approval of the first 3D printed pill, Spritam®, by Aprecia Pharmaceuticals in 2015. This technology has been utilized for the printing of medical devices, dental implants, artificial organs, research prototypes, tailored dosage forms, drug fabrication, and specialty surgical instruments. It offers great flexibility, which justifies its use in a wide range of settings, including educational institutions, hospitals, and even households. Globally, numerous industry experts have predicted the use of 3D printing technology for centralized manufacturing of pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicine, and in the early phases of clinical trials over the span of the next 5 years.
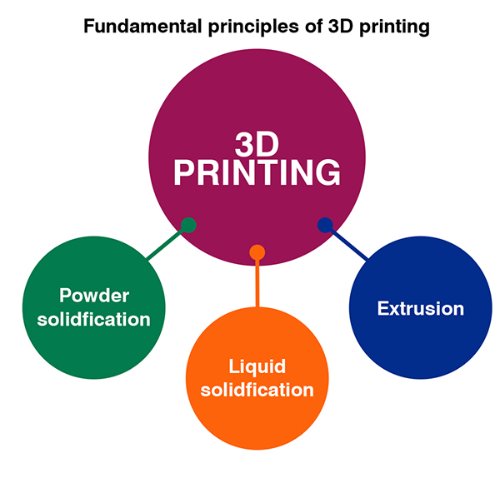
3D printing of pharmaceuticals can be carried out using feed materials like particles, particle colloids, plastic powders, polymers, polymer solutions, gels, polymer-particle composites, or continuous thin sheets.
1. Powder solidification is carried out by techniques like selective laser sintering and binder jetting.
2. Liquid solidification is carried out by the techniques of stereolithography and inkjet printing.
3. Extrusion of the feed material is carried out by techniques of fused deposition modeling and semisolid extrusion.
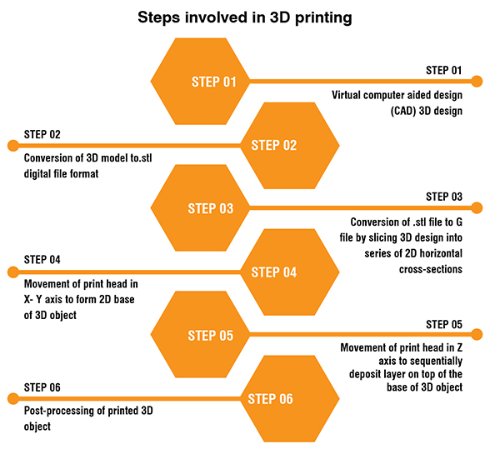
3D printing starts with the creation of a virtual 3D design of the object using digital design software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Autodesk, etc. The steps involved in the 3D printing process are mentioned in the following figure.
3D printing is a promising technology to help achieve the goals of precision medicine and personalized therapy. Immediate-release tablets, chewable tablets, orodispersible films, solid self-emulsifying formulations, microneedles, and hydrogel patches are some of the dosage forms that can be fabricated using 3D printing. A pill containing multiple drugs in the same dosage form can be printed, which will avoid polypharmacy and improve patient compliance. Incompatible drugs can also be fabricated in the same dosage form. The release profiles of the multiple drugs can be modified by using the appropriate release-modifying polymers for the individual drugs. Customized implants and prosthetics can also be printed as per the individual patient’s needs.
Learn more: https://www.pharmafocuseurope.com/information-technology/printing-what-store-medicine-future





















Comments
0 comment