views
Endobronchial Ultrasound Biopsy A Breakthrough Procedure for Diagnosing Lung Diseases
What is Endobronchial Ultrasound Biopsy?
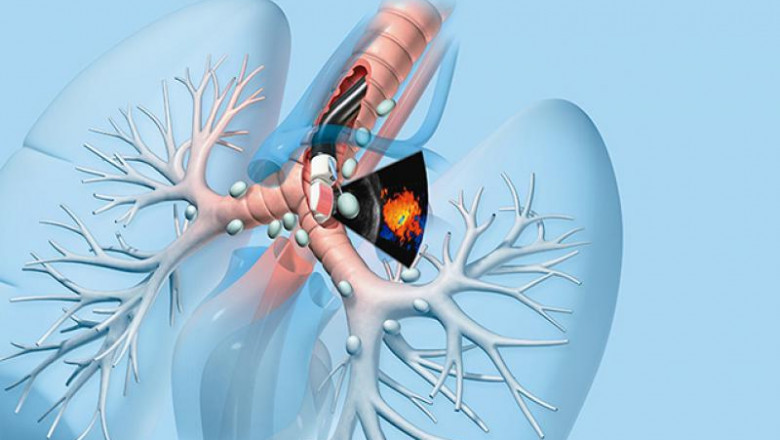
Endobronchial ultrasound biopsy (EBUS-TBNA) is an advanced bronchoscopic technique that obtains samples from the lymph nodes around the lungs (mediastinal lymph nodes) and tissues around the airways (peribronchial tissue) using an ultrasound probe. This allows doctors to precisely guide small needles through the bronchial walls to obtain samples from these normally inaccessible areas.
How is an Endobronchial Ultrasound Biopsy Procedure Performed?
During an Endobronchial Ultrasound Biopsy procedure, patients will be given local anesthesia and mild sedatives. Then, a thin, flexible endoscope called a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into the lungs. Attached to the end of the bronchoscope is a small ultrasound probe that transmits images to a screen. While viewing these images, the doctor passes sterile, hollow needles through the working channel of the bronchoscope. Guided by the ultrasound images, the doctor precisely positions the needles to sample target lymph nodes and tissues. Once in position, the needles are used to extract tiny biopsy samples. Special care is taken to ensure patient comfort and safety throughout the procedure.
What Areas can be Biopsied with EBUS-TBNA?
EBUS allows doctors to obtain samples from areas that cannot be reached during regular bronchoscopy. Some key areas that can be biopsied include:
- Mediastinal lymph nodes: Lymph nodes located in the middle of the chest (mediastinum) can be imaged and sampled with EBUS. This helps diagnose cancers and infections that may have spread from the lungs or other organs.
- Hilar lymph nodes: Lymph nodes located near where the main bronchi branches off the trachea (hilar area) can also be imaged and sampled.
- Peribronchial tissues: Using the ultrasound images as a guide, EBUS needles can obtain samples from lesions or thickened tissues located alongside the main airways (bronchi).
- Pulmonary nodules: In some cases, small nodules located deep in the lungs may be biopsied under EBUS guidance.
Advantages of Endobronchial Ultrasound Biopsy over other Diagnostic Tests
EBUS-TBNA has several advantages compared to older biopsy methods:
- Increased diagnostic accuracy: The real-time ultrasound images provide doctors a live view of the sampling area compared to blind biopsies. This allows them to precisely guide needles to target tissues.
- Safer approach: As samples are obtained directly through the bronchoscope working channel, there is no need for surgical procedures or invasive thoracoscopy. This makes EBUS safer, especially for fragile patients.
- Lower costs: As a minimally invasive outpatient procedure without the need for general anesthesia, EBUS-TBNA has lower procedure costs and shorter hospital stays than alternative tests.
- Reduced sampling error: With ultrasound guidance, EBUS obtains larger biopsy samples from suspicious lesions compared to conventional bronchoscopy. This improves diagnostic yields.
Potential Applications and Uses of Endobronchial Ultrasound Biopsy
Due to its safety, accuracy and minimally invasive nature, EBUS-TBNA is being used increasingly for:
- Lung cancer staging: Determining how far a cancer has spread is important for prognosis and treatment planning. EBUS is very effective for staging by examining mediastinal lymph nodes.
- Sarcoidosis diagnosis: EBUS allows direct visualisation and sampling of enlarged hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes often seen in sarcoidosis patients.
- Lymphoma diagnosis: EBUS helps diagnose lymphomas by examining lymph nodes for malignant cells. It is especially useful for sampling enlarged nodes impalpable on clinical exam.
- Tuberculosis diagnosis: EBUS provides samples to detect mycobacterium tuberculosis from lesions or lymph nodes in the lungs of patients with TB signs.
- Fungal infection diagnosis: In immunocompromised patients, EBUS assists in diagnosing opportunistic fungal infections involving the lungs and lymph nodes.
Future Directions
With improvements in imaging resolution, new biopsy needles and other technological refinements, EBUS capabilities are growing rapidly. It is gradually becoming a one-stop shop for minimally invasive diagnosis and staging of various lung cancers and granulomatous lung diseases. As a safe, accurate and cost-effective procedure, endobronchial ultrasound biopsy use is projected to increase significantly in the coming years. It is transforming how doctors obtain diagnostic samples noninvasively from previously inaccessible areas within the lungs and chest.
Discover the Report for More Insights, Tailored to Your Language:
About Author:
Money Singh is a seasoned content writer with over four years of experience in the market research sector. Her expertise spans various industries, including food and beverages, biotechnology, chemical and materials, defense and aerospace, consumer goods, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/money-singh-590844163)





















Comments
0 comment