Klap: The AI Video Editing Tool Revolutionizing Social Media Content Creation
-


Discover how the best digital marketing agencies are optimizing for voice s...

La RandM Tornado 15000 est une cigarette électronique jetable haut de gamme...

Giocare in Sicurezza sui non AAMS: Cosa Sapere nel 2025
DXB APPS is a mobile app development company providing bespoke, high-qualit...
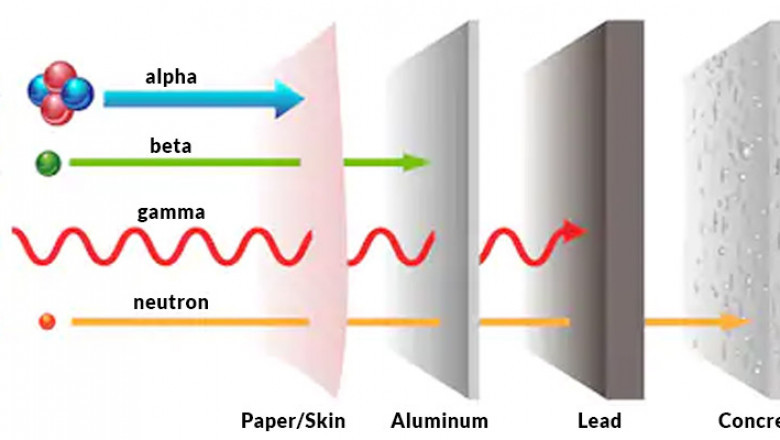
The Global Radiation Shielding Materials Market Size is Expected to Reach U...

Velora Visuals offers premium real estate drone photography in London, Onta...

The Global Health Ingredients Market Size is Projected to Exceed USD 198.8...










