
بررسی جامع سایت تک بت: پیشبینی ورزشی و سرگرمی بینظیر
سایت تک بت یکی از پرطرفدارترین و شناختهشدهترین پلتفرمهای شرطبندی فارسی...
-


سایت تک بت یکی از پرطرفدارترین و شناختهشدهترین پلتفرمهای شرطبندی فارسی...

The Role of Insurance Brokers in Dubai: Guiding Clients Through a Dynamic M...

The Local Charm of Every Grocery Store in Wisconsin
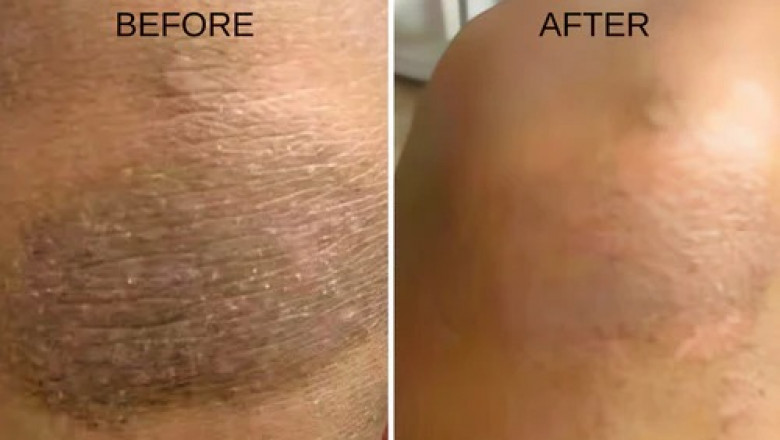
Whether you use it in the morning or before bed, it becomes a comforting pa...

KLM Airlines Atlanta Office is really amazing, if u want safe and comfortab...

At the heart of Khizri’s approach to journalism is a commitment to providin...

Organizations that adopt these learning strategies for 2025 would see an im...

The Pursuit of Luxury: Unlocking the Secrets to a Life of Elegance

