Klap: The AI Video Editing Tool Revolutionizing Social Media Content Creation
-
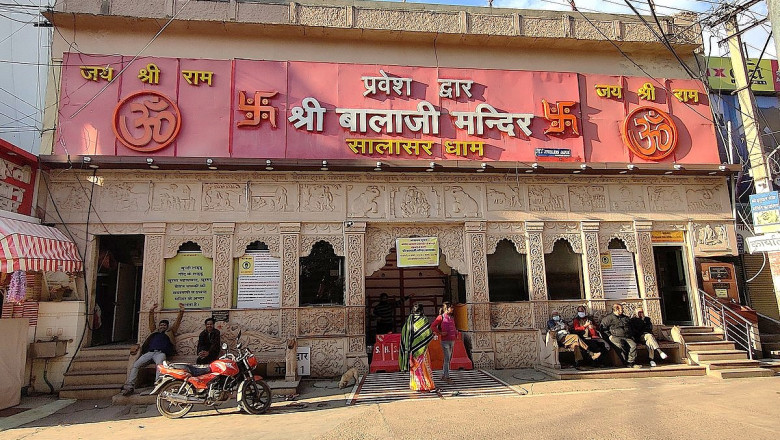


Salasar dham is the place where Hanuman devotees can visit. It is a world-f...

According to Fortune Business Insights Global Waterless Cosmetics Market si...

Global Tea-based Skin Care Market size is expected to be worth around USD 5...

The Synthetic Dyes market was valued at USD 5.8 Billion in 2023 and is proj...

Cash flow is the king in any company, and maintaining it is crucial for per...
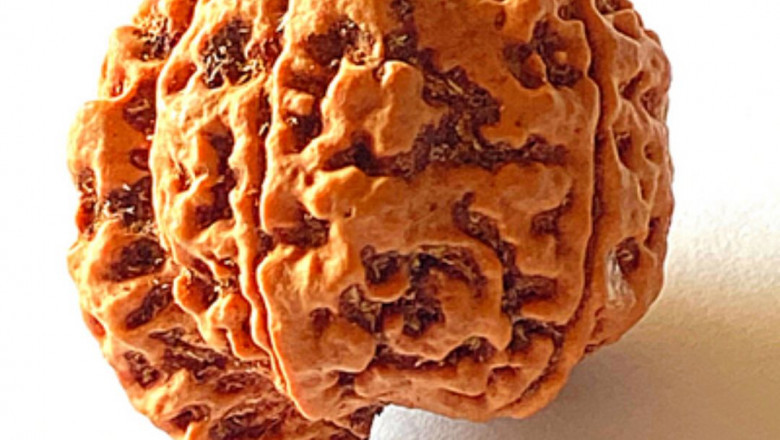
Haridwar, one of the holiest cities in India, stands as a spiritual gateway...
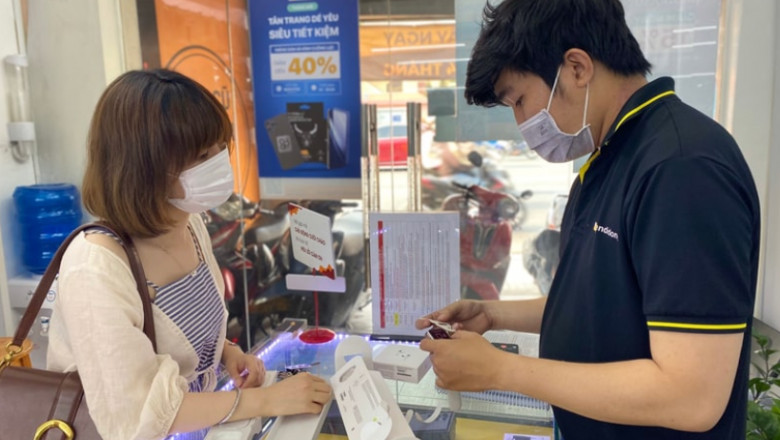

Thay Pin iPhone XS Max chính hãng giá bao nhiêu? Làm sao để đảm bảo an toàn...
