Klap: The AI Video Editing Tool Revolutionizing Social Media Content Creation
-


Rennee Foods is dedicated to bringing you a diverse range of high-quality c...

Uncover the growing importance of software in health care and how it drives...
The global Limiter Diodes Market size was valued at US$ 163.4 million in 20...

The transplantation market research report highlights market research and i...

Turn your moments into masterpieces with Senses at Play, the trusted name a...

The ADC exam preparation process is a critical phase for any internationall...
With the rising demand for privacy and convenience, the STD test at home Du...
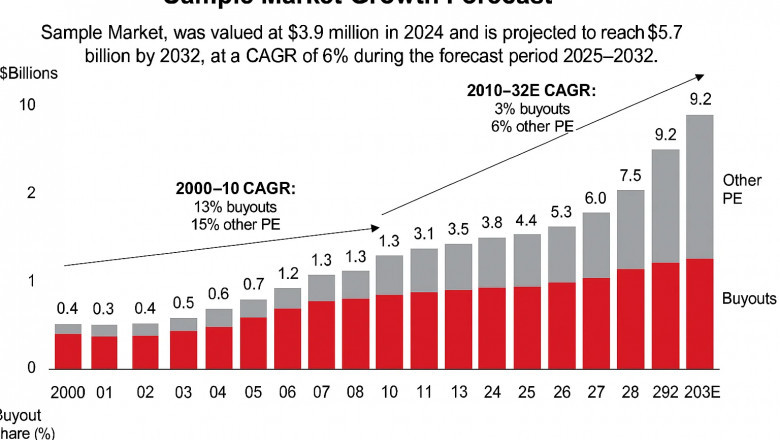
Global Initiator TAEC Market shows steady expansion, valued at US$21.2 mill...
